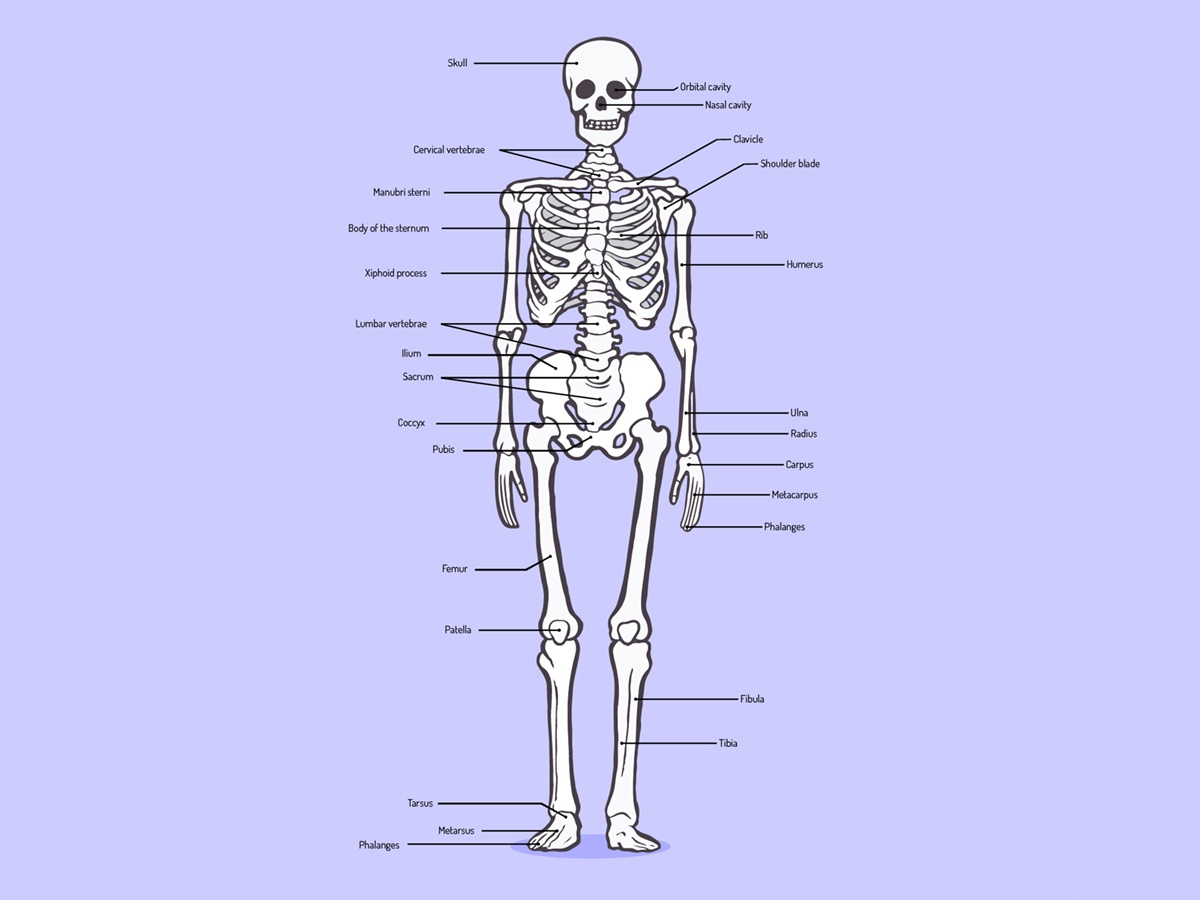
The thought of breaking a bone is enough to make most of us squirm, but the science behind the injuries is actually quite fascinating. Our skeletal system is made up of 206 bones, as well as tissue, blood vessels, and nerves that all need to work together. Bones have adapted over time to provide support for the body, anchor muscles and allow them to contract, and allow limbs to move. Additionally, bones act as the body’s source of calcium and are always going through changes under the control of hormones. Because of these things, bones are vulnerable to a large variety of injuries. But, what happens to our bodies when a bone breaks?
How do bones break?
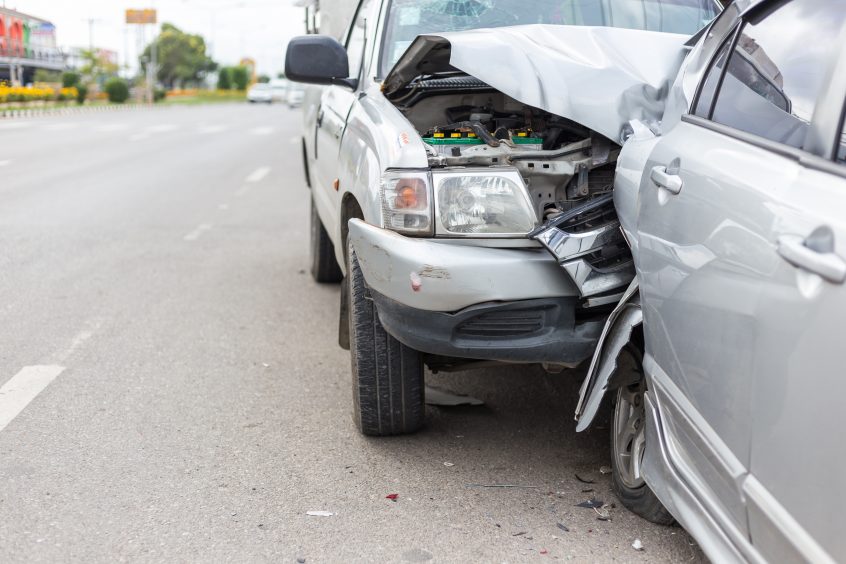
When outside forces are applied to a bone, it has the potential to fail because the bone cannot withstand the pressure from those external factors. The type of force on the bone may determine the type of injury that occurs. There are several reasons why broken bones hurt: the nerve endings that contain fibers are irritated, broken bones bleed and the blood and swelling causes pain, and muscles surrounding the area may spasm as a result of trying to hold the fragmented bones together. Injuries are based on the location of the injury on the bone, how the bone fragments are aligned, and whether any other complications exist.
How does the body react to a break?
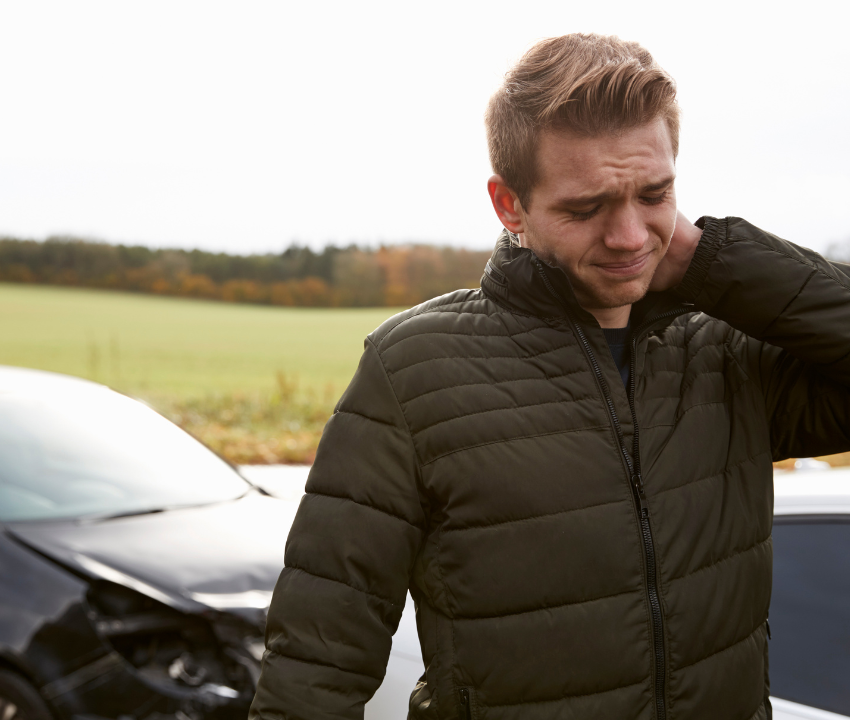
It is not uncommon for a person to feel dizzy or groggy after breaking a bone, and sometimes people feel cold as their body goes into shock. Within a few hours of your bone breaking, the body forms a clot around the break. Immune system cells in the blood clot get rid of germs that may have entered. Cells called chondroblasts create a soft collagen callus around the break area and a hard callus eventually replaces the soft callus, creating new bone. During the final stage of healing, the extra bone that was created around the hard callus gets broken down, returning the bone to its original shape.
Once a break has healed and a cast has been removed, a patient may experience dry skin where their body part has been covered for so long. They may also notice a lack of muscle definition in that area, but the good news is this can be built back up over time. Our muscles will atrophy and shrink when not in use for a prolonged period of time, and part of the healing process involves strengthening these muscles back up.
If you think you may be suffering from a break, or bone injury, call the Clinic at 210-342-2777 or request an appointment online.